spring-boot-starter-validation
25410 开源 | 2023-3-27-
编写程序Controller接口时,对于参数的验证非常重要,但是多个参数时,如果我们使用IF-ELSE挨个判断,那么程序会非常累赘,此时我们可以考虑使用Spring的Validtion框架,使用注解的方式优雅的编写参数格式的验证。
引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId> </dependency>
参数说明:
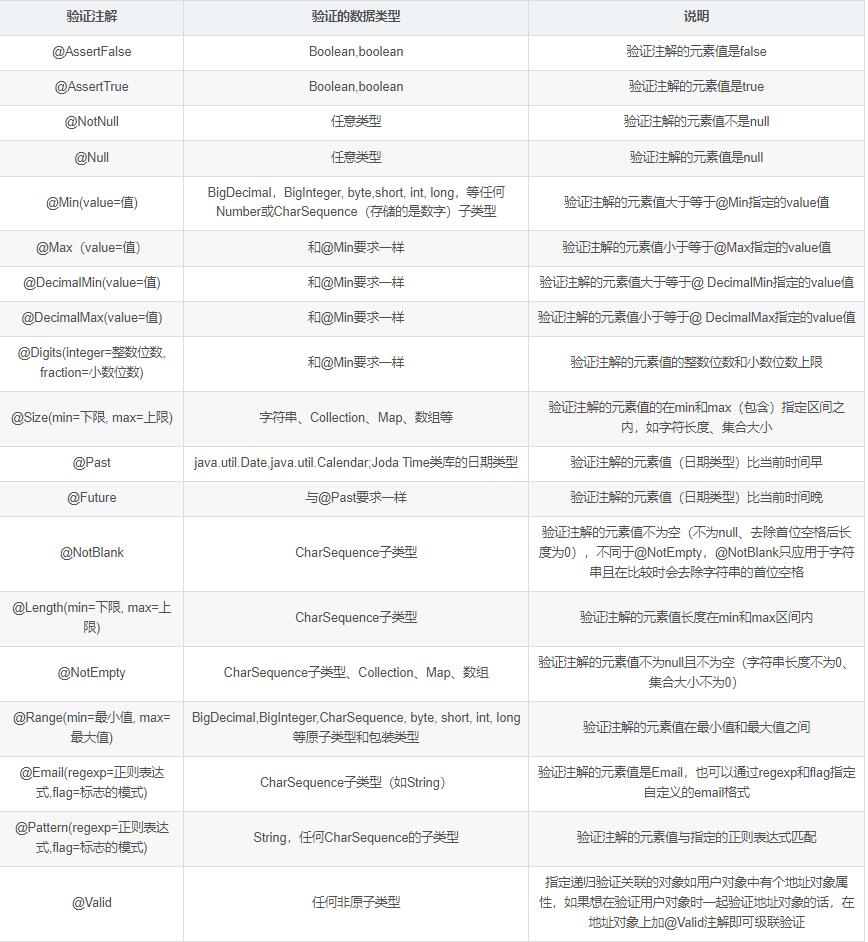
可以总结一下这些注解的用途
空检查 @Null 验证对象是否为null @NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串 @NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格. @NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY. Booelan检查 @AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true @AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false 长度检查 @Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内 @Length(min=, max=) 验证注解的元素值长度在min和max区间内 日期检查 @Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前 @Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后 @Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则 数值检查,建议使用在Stirng,Integer类型,不建议使用在int类型上,因为表单值为“”时无法转换为int,但可以转换为Stirng为"",Integer为null @Min 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值 @Max 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值 @DecimalMax 被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示.小数存在精度 @DecimalMin 被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表示.小数存在精度 @Digits 验证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法 @Digits(integer=,fraction=) 验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字,interger指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度。 @Range(min=, max=) 验证注解的元素值在最小值和最大值之间 @Range(min=10000,max=50000,message="range.bean.wage") @Valid 写在方法参数前,递归的对该对象进行校验, 如果关联对象是个集合或者数组,那么对其中的元素进行递归校验,如果是一个map,则对其中的值部分进行校验.(是否进行递归验证) @CreditCardNumber信用卡验证 @Email 验证是否是邮件地址,如果为null,不进行验证,算通过验证。 @ScriptAssert(lang= ,script=, alias=) @URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)
编写示例代码
package com.example.springboot.model; import lombok.Data; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Length; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Range; import javax.validation.Valid; import javax.validation.constraints.*; import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; /** * Validation类的相关注解及描述 */ @Data public class ParaCheck { // 验证注解的元素值是true @AssertTrue private Boolean isBoolean; // 验证注解的元素值不是null @NotNull private String notNull; // 验证注解的元素值是null @Null private String isNull; // 验证注解的元素值大于等于@Min指定的value值 @Min(value=0) @Max(value = 100) private long min; // 验证注解的元素值大于等于@DecimalMin指定的value值 @DecimalMin(value="0") @DecimalMax(value="100") // 验证注解的元素值的整数位数和小数位数上限 @Digits(integer=3, fraction=2) private BigDecimal bigMin; // 验证注解的元素值的在min和max(包含)指定区间之内,如字符长度、集合大小 @Size(min=1, max=100, message = "没有传递任何内容") private List<String> list; // 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间早 @Past // 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间晚 // @Future private Date date; // 验证注解的元素值不为空(不为null、去除首位空格后长度为0),不同于@NotEmpty,@NotBlank只应用于字符串且在比较时会去除字符串的首位空格 @NotBlank(message = "内容不能为空") private String notBlank; // 验证注解的元素值长度在min和max区间内 @Length(min=5, max=15, message = "姓名长度在5-15") private String name; // 验证注解的元素值不为null且不为空(字符串长度不为0、集合大小不为0) @NotEmpty(message = "字符串不能为空") private String notEmpty; // 验证注解的元素值在最小值和最大值之间 @Range(min=1, max=100, message = "数值设置区间为1-100") private long range; // 验证注解的元素值是Email,也可以通过regexp和flag指定自定义的email格式 @Email private String email; @Pattern(regexp = "/^1[3-9]\\d{9}$/", message = "手机号格式不正确") // 验证注解的元素值与指定的正则表达式匹配 private String phone; // 指定递归验证关联的对象如用户对象中有个地址对象属性 @Valid private Blog blog; }Controller层面使用
package com.example.springboot.controller; import com.example.springboot.model.ParaCheck; import com.google.gson.Gson; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/test/") public class XssController { @PostMapping("/checkPara") public String checkPara(@RequestBody ParaCheck paraCheck){ Gson gson = new Gson(); System.out.println("收到参数:" + gson.toJson(paraCheck)); return "ok"; } }END
推荐您阅读更多有关于“ spring 注解 参数 Validation 检验 ”的文章
-
猜你喜欢
- 个人资料
-

Java小强
未曾清贫难成人,不经打击老天真。
自古英雄出炼狱,从来富贵入凡尘。
- 站内搜索
-
- 文章分类
- 最新文章
- 热门文章
发表评论: