Centos7上Redis主从集群数据迁移
43232 软件 | 2022-1-25-
Centos7上Redis主从集群(http://www.javacui.com/tool/591.html)最后提到一点,集群时无需再进行配置哨兵模式,集群会进行自动故障转移。
那么如何进行数据迁移,做到无感知机器切换呢?
利用cluster failover命令可以手动让集群中的某个master宕机,切换到执行cluster failover命令的这个slave节点,实现无感知的数据迁移。其流程如下
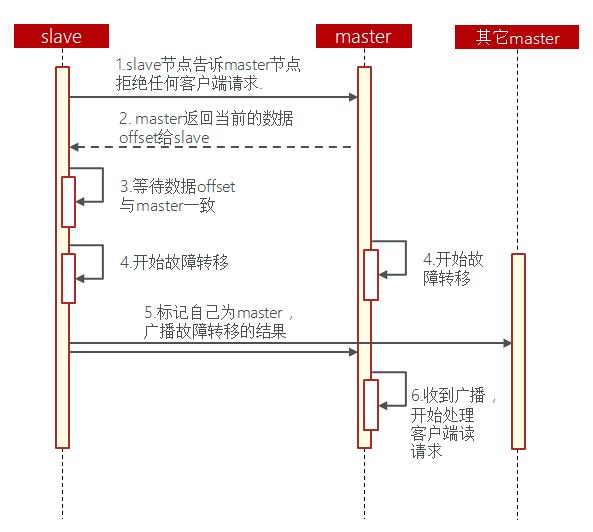
手动的Failover支持三种不同模式:
缺省:默认的流程,如图1~6歩
force:省略了对offset的一致性校验
takeover:直接执行第5歩,忽略数据一致性、忽略master状态和其它master的意见。
具体操作流程为
1.准备一个新机器B,作为主机A的从机slave。
2.在新机器B上执行cluster failover。
3.新机器B做master后,更新原来master设备A。
4.更新A后让A作为B的slave,然后让A夺回master即可。
这里接着之前的7002停机,重新启动,然后执行failover:
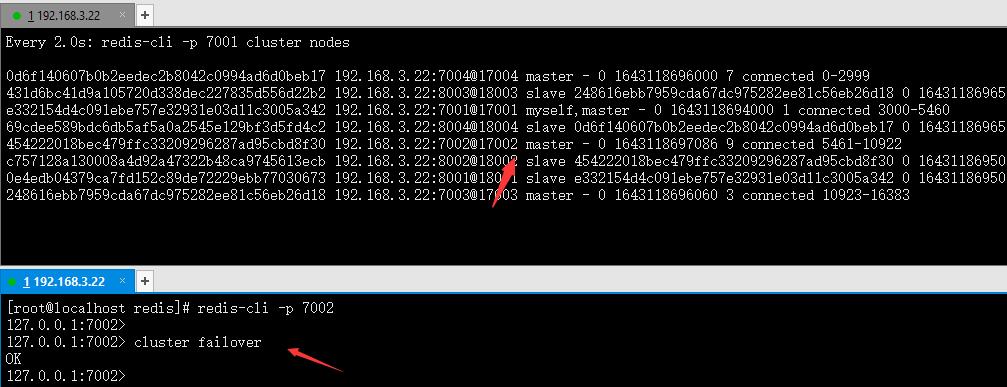
可以看到7002已经成为master节点。
-
猜你喜欢
评论:
回复
Java小强 评论于 2022-01-25 21:57
FORCE option: manual failover when the master is down
The command behavior can be modified by two options: FORCE and TAKEOVER.
If the FORCE option is given, the replica does not perform any handshake with the master, that may be not reachable, but instead just starts a failover ASAP starting from point 4. This is useful when we want to start a manual failover while the master is no longer reachable.
However using FORCE we still need the majority of masters to be available in order to authorize the failover and generate a new configuration epoch for the replica that is going to become master.
TAKEOVER option: manual failover without cluster consensus
There are situations where this is not enough, and we want a replica to failover without any agreement with the rest of the cluster. A real world use case for this is to mass promote replicas in a different data center to masters in order to perform a data center switch, while all the masters are down or partitioned away.
The TAKEOVER option implies everything FORCE implies, but also does not uses any cluster authorization in order to failover. A replica receiving CLUSTER FAILOVER TAKEOVER will instead:
Generate a new configEpoch unilaterally, just taking the current greatest epoch available and incrementing it if its local configuration epoch is not already the greatest.
Assign itself all the hash slots of its master, and propagate the new configuration to every node which is reachable ASAP, and eventually to every other node.
Note that TAKEOVER violates the last-failover-wins principle of Redis Cluster, since the configuration epoch generated by the replica violates the normal generation of configuration epochs in several ways:
There is no guarantee that it is actually the higher configuration epoch, since, for example, we can use the TAKEOVER option within a minority, nor any message exchange is performed to generate the new configuration epoch.
If we generate a configuration epoch which happens to collide with another instance, eventually our configuration epoch, or the one of another instance with our same epoch, will be moved away using the configuration epoch collision resolution algorithm.
Because of this the TAKEOVER option should be used with care.
The command behavior can be modified by two options: FORCE and TAKEOVER.
If the FORCE option is given, the replica does not perform any handshake with the master, that may be not reachable, but instead just starts a failover ASAP starting from point 4. This is useful when we want to start a manual failover while the master is no longer reachable.
However using FORCE we still need the majority of masters to be available in order to authorize the failover and generate a new configuration epoch for the replica that is going to become master.
TAKEOVER option: manual failover without cluster consensus
There are situations where this is not enough, and we want a replica to failover without any agreement with the rest of the cluster. A real world use case for this is to mass promote replicas in a different data center to masters in order to perform a data center switch, while all the masters are down or partitioned away.
The TAKEOVER option implies everything FORCE implies, but also does not uses any cluster authorization in order to failover. A replica receiving CLUSTER FAILOVER TAKEOVER will instead:
Generate a new configEpoch unilaterally, just taking the current greatest epoch available and incrementing it if its local configuration epoch is not already the greatest.
Assign itself all the hash slots of its master, and propagate the new configuration to every node which is reachable ASAP, and eventually to every other node.
Note that TAKEOVER violates the last-failover-wins principle of Redis Cluster, since the configuration epoch generated by the replica violates the normal generation of configuration epochs in several ways:
There is no guarantee that it is actually the higher configuration epoch, since, for example, we can use the TAKEOVER option within a minority, nor any message exchange is performed to generate the new configuration epoch.
If we generate a configuration epoch which happens to collide with another instance, eventually our configuration epoch, or the one of another instance with our same epoch, will be moved away using the configuration epoch collision resolution algorithm.
Because of this the TAKEOVER option should be used with care.
回复
Java小强 评论于 2022-01-25 21:56
This command, that can only be sent to a Redis Cluster replica node, forces the replica to start a manual failover of its master instance.
A manual failover is a special kind of failover that is usually executed when there are no actual failures, but we wish to swap the current master with one of its replicas (which is the node we send the command to), in a safe way, without any window for data loss. It works in the following way:
The replica tells the master to stop processing queries from clients.
The master replies to the replica with the current replication offset.
The replica waits for the replication offset to match on its side, to make sure it processed all the data from the master before it continues.
The replica starts a failover, obtains a new configuration epoch from the majority of the masters, and broadcasts the new configuration.
The old master receives the configuration update: unblocks its clients and starts replying with redirection messages so that they'll continue the chat with the new master.
This way clients are moved away from the old master to the new master atomically and only when the replica that is turning into the new master has processed all of the replication stream from the old master.
A manual failover is a special kind of failover that is usually executed when there are no actual failures, but we wish to swap the current master with one of its replicas (which is the node we send the command to), in a safe way, without any window for data loss. It works in the following way:
The replica tells the master to stop processing queries from clients.
The master replies to the replica with the current replication offset.
The replica waits for the replication offset to match on its side, to make sure it processed all the data from the master before it continues.
The replica starts a failover, obtains a new configuration epoch from the majority of the masters, and broadcasts the new configuration.
The old master receives the configuration update: unblocks its clients and starts replying with redirection messages so that they'll continue the chat with the new master.
This way clients are moved away from the old master to the new master atomically and only when the replica that is turning into the new master has processed all of the replication stream from the old master.
- 个人资料
-

Java小强
未曾清贫难成人,不经打击老天真。
自古英雄出炼狱,从来富贵入凡尘。
- 站内搜索
-
- 文章分类
- 最新文章
- 热门文章
发表评论: